Deploy an Express.js App to Vercel — A Step By Step Guide
Updated
TL;DR
Vercel is a platform to host frontend applications and static sites but you can also host an Express application using serverless functions.
You can also use Vercel Postgres which allows you to integrate hosted serverless PostgreSQL database such as neon.tech (Neon got acquired by Databricks) accessible by serverless functions.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to create an Express app from scratch and deploy it to vercel.
This article has been updated with latest vercel configurations.
Prerequisites #
Node.js should be installed on your system. To check if it is, run node -v in your terminal and you should get a node version as an output.
Creating an Express App #
Run
npm init -yto create apackage.jsonfile with default configuration.Run
git initto initialize agitrepository.Create a
.gitignorefile and write the folder namenode_modulesin it. You can add as many files and folders you prefer to be ignored bygit.Install the express package using npm or yarn.
npm i expressCreate an
apifolder (in the root folder) and addindex.jsfile in it. Adding an "api" folder is necessary because Vercel treats all index.js files in that folder as serverless functions. So, for example, if you createapi/test/index.js, when you hit<BASE_URL>/testit will execute the code inside api/test/index.js as a serverless function. It is crucial for deploying the express app to Vercel.Update
package.jsonfile to explicitly set the entry file.
{
"name": "test",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "api/index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.21.2"
}
}- Inside the
api/index.jsfile, add the following code in order to create an express app.
// cjs
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000);- Now, add a
GETrequest handler and send a response.
// api/index.js
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send("Express App Responded");
})- Export the
appfor it to be run as a serverless function.
// api/index.js
module.exports = app- Add a
startscript topackage.jsonfile in order to run the application locally.
{
"name": "test",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "api/index.js",
"scripts": {
"script": "node api/index.js",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.21.2"
}
}- Run the application using the command
npm startThe application should be live athttp://localhost:3000.
Recommended ✨
You should get an output similar to the following:

Yayy! You just created an Express.js Application. 🎉
Deploying to Vercel #
Create a
vercel.jsonfile in the root folder of your application. This is a configuration file for Vercel.Add the following to your
vercel.jsonfile, so that every request is routed to/apiendpoint because that where the express app as a serverless function lives.
{
"rewrites": [
{
"source": "/(.*)",
"destination": "/api"
}
]
}Create a
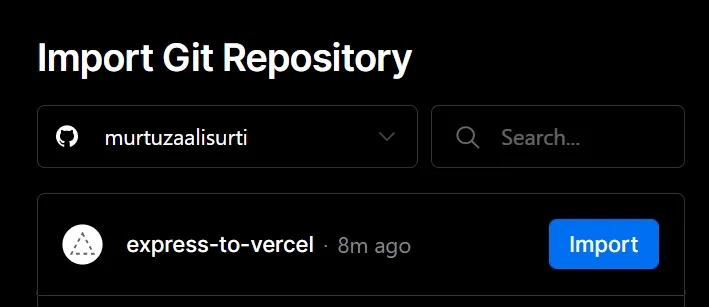
gitrepository on GitHub and add your code to it.Create a new project on Vercel and import the
gitrepository that you just made.
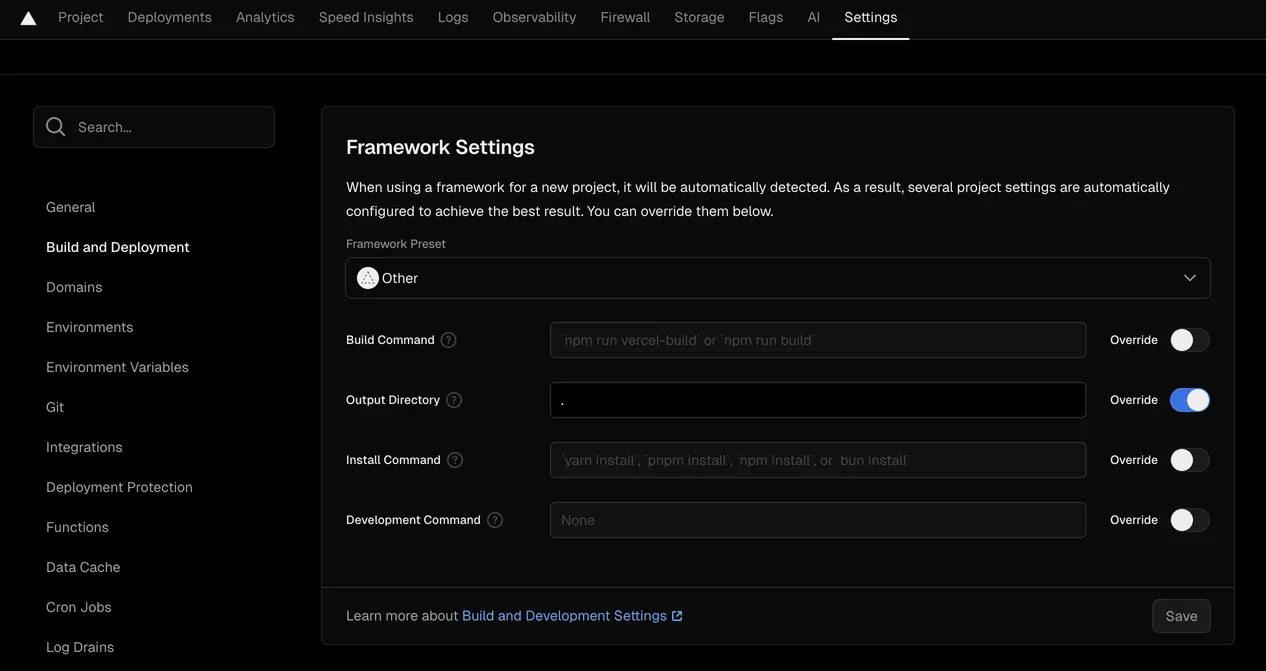
- Go to the project Settings > Build and Deployment > Framework Settings and override the default output directory with the root directory
.. The reason of doing so is to tell Vercel to look for production ready files here. If you intend to use typescript, then the output directory will be the directory in which your compiled files are stored.
Deploy the application.
Your application should now be live! 🎉
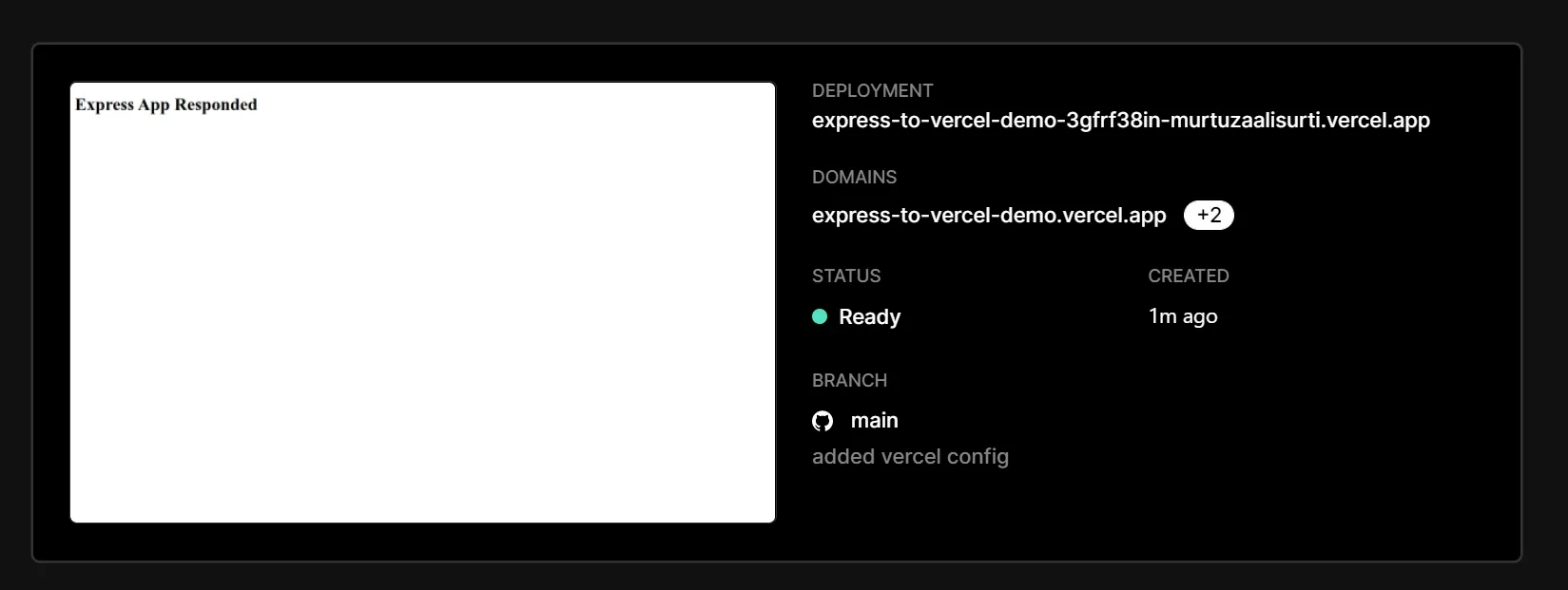
Here's the live demo of the application. You can also find the source code on my express-to-vercel github repository!